Understanding Insulin Syringe Measurements for Accurate Dosage
Insulin Dosage and Syringe Calibration
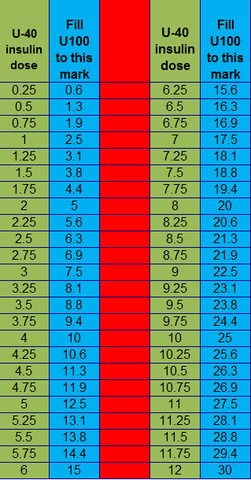
When it comes to **insulin administration**, understanding **insulin syringe** measurements is vital for effective diabetes management. Insulin syringes are specially calibrated to dispense insulin in units rather than milliliters (mL). This distinction is crucial for accurate dosing, as **different types of insulin** come in various concentrations. The most common concentration is **U-100 insulin**, where one milliliter contains 100 units of insulin, making conversion straightforward. However, for concentrations such as **U-40 insulin**, where 1 mL equals 40 units, a different calculation applies. This means 1 unit would equal 0.025 mL. Proper knowledge of these conversions can help avoid potential mistakes and ensure **accurate insulin dosing**.
Understanding Insulin Units and Concentrations
Insulin measurements rely heavily on the concentration formulation of the specific insulin type being used. The key concentrations such as **U-100** and **U-40** demonstrate this principle. With **U-100 insulin**, each unit equates to 0.01 mL, which means if a patient requires 20 units, they must draw up 0.2 mL into the syringe. Conversely, the **U-40 concentration** suggests that patients would need 0.5 mL to deliver the same quantity of insulin. Familiarizing oneself with **insulin concentrations** and their respective conversions plays a crucial role in practical diabetic care and helps in the understanding of **insulin measurements**.
Measuring Insulin Dosages Correctly
Proper **insulin dosage calculation** is fundamentally important for effective diabetes management. Patients should always refer to their healthcare provider’s instructions regarding **insulin dosage guidelines**. For instance, if a diabetic is instructed to administer **30 units of insulin**, using a **U-100 syringe** would mean they should draw 0.3 mL. The potential errors in measurements could lead to *hyperglycemia* or *hypoglycemia*, both serious conditions in diabetes management. Patients might also use an **insulin dosage calculator** for further assistance in determining their exact needs, ensuring that they are adhering to their prescribed regimen accurately.
Types of Insulin Syringes and Their Uses
Various types of **insulin delivery systems** exist to accommodate different treatment needs, from **insulin pens** to traditional syringes. The type of **syringe ml capacity** also varies, which is crucial in determining how to manage insulin effectively. For instance, while pre-filled insulin pens offer convenience and precision in dosing, traditional insulin syringes allow for more flexibility in dosage adjustments. Understanding these tools and how the **syringe labeling** differs can significantly improve insulin management and help people with diabetes make informed decisions regarding their treatment plans.
How to Choose the Right Insulin Syringe
Selecting the appropriate insulin syringe must consider factors such as the prescribed insulin concentration and dosage requirements. A common standard for adults using **U-100 insulin** is a 1 mL syringe, but for children or injectors needing smaller doses, lower capacity syringes (such as 0.5 mL or 0.3 mL) may be more suitable. Understanding which **insulin syringe types** to use helps in managing both parameters effectively, contributing positively to blood sugar control. Consult with a healthcare provider to evaluate what’s best according to individual needs.
Proper Injection Techniques for Insulin Administration
Employing correct **injection techniques** when using an insulin syringe impacts treatment effectiveness significantly. Utilizing a clean syringe and ensuring the proper angle—often preferred at 90 degrees for most patients—can aid in successful absorption. Additionally, rotating **insulin sites of injection** regularly prevents lipodystrophy, a condition where fat tissue develops lumps or hollows that impact insulin absorption and efficacy over time. Techniques such as pinching the skin and inserting the needle swiftly can reduce discomfort and enhance experience during insulin administration.
The Importance of Accurate Insulin Testing
Accurate testing of blood glucose levels is essential for effective **diabetes management**. Knowing your blood sugar helps determine the required **insulin dosage** before meals and snacks. An understanding of the interplay between **blood glucose and insulin** can guide optimum dosing strategies and enhance **glycemic control**. Testing imbues power into your daily treatment routine by allowing you to respond self-adaptively to your body’s needs, ultimately improving overall health outcomes.
Regular Use of Blood Glucose Meters
Routine monitoring with a quality blood glucose meter empowers decision-making regarding **insulin administration**. Many modern devices offer integrated systems that can deliver results quickly and accurately, even syncing with smartphone applications for efficient tracking. This technological advancement not only facilitates easy adjustments for **insulin titration** depending on glucose levels but also supports lifestyle interventions aimed at maintaining optimal health. Additionally, using these tools can foster educational opportunities surrounding diabetes care.
Creating a Diabetes Management Plan
An effective **diabetes management plan** combines proper insulin administration techniques with lifestyle changes. For example, maintaining a healthy diet inclusive of managing carbohydrate intake complements insulin dosing efforts. Engaging in physical activity consistently further amplifies the body’s ability to utilize insulin effectively. Healthcare providers can assist in developing individualized treatment plans that include monitoring insulin levels, understanding blood sugar targets, and planning meal schedules appropriately. The key lies in consistency and strategic management tactics that foster a balanced lifestyle.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding insulin concentrations is crucial for accurate dosing.
- Proper selection of insulin syringes impacts patient care and outcomes.
- Utilizing blood glucose monitoring tools supports informed insulin administration.
- Healthy lifestyle choices complement insulin therapy in diabetes management.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between U-100 and U-40 insulin?
The primary difference between U-100 and U-40 insulin lies in their concentrations. **U-100 insulin** contains 100 units of insulin per 1 mL, while **U-40 insulin** consists of 40 units per mL. This notable variation dictates how insulin is measured in syringes; thus, patients must pay careful attention to syringe markings to ensure they draw the correct dosage.
2. How should I store my insulin effectively?
Proper **insulin storage guidelines** include keeping insulin vials in a refrigerator and away from direct sunlight or heat sources. It’s essential not to freeze the insulin, as this can damage its effectiveness. Once opened, many insulins can be stored at room temperature for a certain period, often 28 days, but always consult the product insert for specific storage instructions.
3. How can I reduce pain during insulin injections?
To minimize pain during injections, it’s recommended to use a smaller gauge needle, inject at a 90-degree angle in a pinch of skin, and rotate injection sites frequently. Additionally, **insulin administration** in a warmer environment can help in easing the process by relaxing the skin. Proper technique is essential for minimizing discomfort during injections.
4. What are the common mistakes in insulin dosing?
Common mistakes in **insulin dosing** may include miscalculating units based on the syringe used, forgetting to check blood glucose levels prior to administering insulin, and failing to account for variations in insulin absorption. To prevent these errors, patients should always double-check the concentration of insulin and their enrolled dosage with healthcare providers.
5. Can insulin be administered using a pen?
Yes, **insulin pens** are an efficient and user-friendly alternative for **insulin administration**. These pens can dispense precise dosages without requiring traditional syringes which may promote better adherence. Most pre-filled pens today contain various **types of insulin**, making the management of diabetes simpler and more accessible.
6. How often should I test my blood glucose levels?
The frequency of blood glucose testing should be tailored to the individual’s diabetes management plan. Many healthcare providers recommend testing multiple times a day for those using insulin, particularly before meals and bedtime. Regular testing helps in adjusting **insulin dosages** accordingly and enhancing overall blood sugar control.