“`html
How to Effectively Find Domain and Range of a Graph
Understanding Domain and Range
In mathematics, **domain** and **range** are vital concepts when analyzing a **graph**. The **domain of a function** refers to the set of all possible input values, or **x-values**, while the **range of a function** describes the set of all possible output values, or **y-values**. Effectively identifying the **domain** and **range** involves a series of steps, including interpreting the graph, recognizing any **restrictions**, and determining the behavior of the **function** represented. By ensuring a clear grasp of these concepts, one can enhance their skills in **graph analysis** and help illustrate the relationship between variables.
Identifying Domain
To determine the **domain**, start by examining the **graph** for any visible restrictions. Graphs of functions can exhibit various traits such as vertical asymptotes or gaps indicating that certain **x-values** are not included. **Continuous functions**, for instance, generally feature a **domain** that spans all real numbers unless restrictions are applied. One technique often employed is the **vertical line test**, where a vertical line is passed through the **graph**; if it intersects the **graph** more than once, the function fails the test, signaling a more complex **domain**. Hence, sketching the graph on a coordinate system can aid significantly in visualizing the **domain** of the function.
Types of Intervals
Domains can also be expressed in terms of **intervals**, which provide a concise representation of the valid input values. The **domain** can be divided into several types: **bounded intervals**, where both endpoints are finite, or **unbounded intervals** that extend to infinity in one or both directions. To visualize domain restrictions effectively, consider examples such as **piecewise functions**. Each segment of the function could provide different **domains**, requiring examination of each part separately to derive a complete understanding of the overall **domain**.
Practical Example: Determining Domain
Consider the **function** f(x) = 1/(x – 3), which presents a **vertical asymptote** at **x = 3**, thus impacting the **domain**. The effective **domain** this function is defined as all real numbers except for **x = 3**. This notation can be expressed mathematically in interval notation as (-∞, 3) ∪ (3, ∞). By applying methods of analyzing graphs, one can determine that, for each **x-value** in the defined intervals, there are corresponding output values of the function. Such categorization of input **x-values** highlights the importance of clear identification techniques in discovering the **domain**.
Finding Range of a Function
Having established the **domain**, the next crucial step is to determine the **range** of a graph. The **range of a function** indicates all possible **y-values** that correspond to the inputs in the **domain**. It is essential to visualize how the function behaves throughout the **domain**, allowing us to assess output values. Utilizing both the **horizontal line test** and examining the maximum and minimum points on the graph can further assist in discovering the complete set of outputs.
Behavioral Analysis of Functions
The behavior of **functions** is categorized by distinguishable features such as increasing, decreasing, or constant intervals. For instance, for a parabola facing upwards, every **input value** corresponds to an output that starts from a minimum value and increases to positive infinity. This understanding of function dynamics enables better prediction of **y-values** across the graph. By analyzing critical points like local maxima and minima, it becomes easier to define the full **range** of the function.
Examples of Range Determination
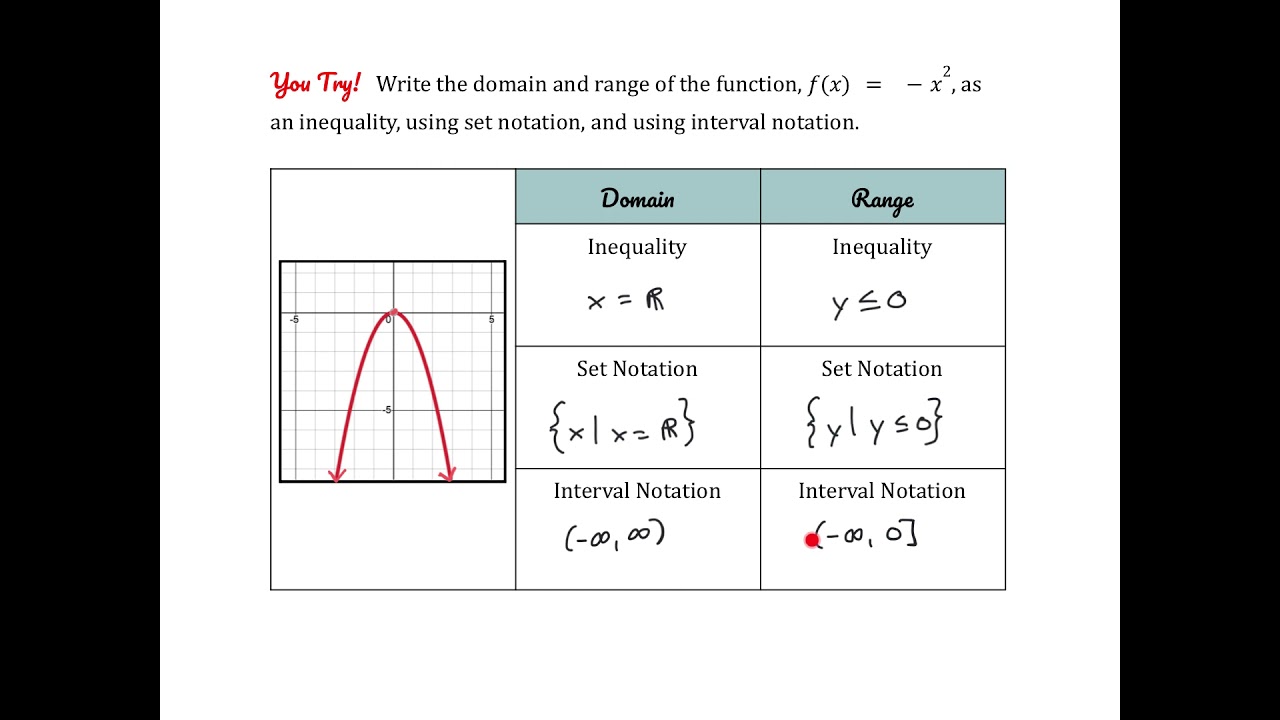
A **function** like g(x) = x² exhibits a clear behavior with a minimum **y-value** of 0 and extends to positive infinity. Thus, the **range** can be notated in interval form as [0, ∞). Structuring such conclusions provides a seamless method for interpreting any potential outputs from the **functions** on the graph, allowing students to refine their graph interpretation skills significantly. The ability to recognize continuous versus discrete outputs also plays a pivotal role in determining exact possible **y-values**.
Determining Output Values
When evaluating for output values, a stepwise approach can simplify the process. Begin with analyzing the graph for patterns in the **y-values**. This complex yet truthful relation between the **input values** and corresponding **output values** showcases an **input-output mapping**, ideally suited for function evaluation exercises. Throughout this process, establishing clear reasoning behind each step and results of analysis enhances comprehension of underlying mathematical principles.
Visual Representation Techniques
Utilizing visual techniques can significantly empower **finding domain** and **range** values. Graphs not only illustrate the **domain** and **range**, but they also reinforce learners’ understanding through practical visual outputs. Graphing techniques such as plotting critical points, noting transformations, and observing shifts offer robust visual cues.
Graphing Techniques for Accuracy
Different methods yield various insights into the graph’s features. For example, identifying **vertical shifts** can indicate how the **range** is altered compared to functions without shifts. Making use of **graphing calculators** or **software tools** can help automate these processes and enhance accuracy to find the **domain** and **range** quickly. In this digital age, combining technology with traditional mathematical methods forms a complete pathway to enhanced learning and interpretation.
Annotations on Graphs as Additional Support
Another beneficial method is utilizing annotations on the graphs to mark important points relating to the **domain** and **range**. Labeling discontinuities, intervals, and critical points guides learners in noticing significant factors affecting the entire structure. Such graphical notes can serve as reminders representing the concepts behind finding both aforementioned metrics. This visual support amplifies understanding in the context of mathematical instructions.
Conclusion
Mastering the process of effectively finding the **domain** and **range** of a graph is essential in understanding mathematical functions and their applications. This guide has provided valuable steps and strategies for clear identification of **domain** and **range**, as well as insight into behavioral dynamics with practical examples and visual representation techniques.
Key Takeaways
- Recognize the importance of **domain** and **range** in graph analysis.
- Understand and apply techniques like vertical and horizontal line tests to determine function behaviors.
- Utilize technology for precise graphing and interval notation to clarify findings.
- Approach both **domain** and **range** through various methods, including visual aids for enhanced comprehension.
FAQ
1. What is the importance of identifying domain and range?
Identifying **domain** and **range** is crucial as it dictates the input and output values of a **function**. Understanding these parameters not only aids in evaluating mathematical problems but also ensures correctness in function considerations, enhancing overall comprehension of math concepts.
2. How can I quickly determine the domain of complex graphs?
To determine the **domain** efficiently, employ the **vertical line test** to spot restrictions, analyze any asymptotes, and use interval notation to summarize valid **x-values**. This method streamlines the identification process.
3. Can discrete functions have domain or range restrictions?
Yes, discrete functions often have specific restrictions in their **domain** and **range** according to the defined points, ensuring that they only include distinct **x-values** and **y-values** without any gaps in between.
4. What are some common notations for intervals in domain and range?
The common notations for **domain** and **range** express intervals in closed form [a, b], and open form (a, b). Familiarity with these forms allows clearer communication of these mathematical concepts.
5. How do transformations affect the domain and range of a function?
Transformations such as shifts, stretches, or reflections impact the **domain** and **range** significantly. For instance, vertical shifts affect the **range**, while horizontal shifts affect the **domain**, modifying the entire structure of the function.
“`