How to Find LCM: Smart Methods for 2025 Challenges
Understanding the Basics of LCM
Before delving into how to find LCM, it’s important to grasp the concept of **Least Common Multiple** (LCM). The LCM of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of all the numbers. For example, the **LCM of two numbers** like 4 and 5 is 20, since 20 is the first number that both 4 and 5 divide without a remainder. Understanding LCM is crucial in various fields; from solving mathematical problems to applying it in real-life challenges. A vital aspect of finding LCM is learning different methods to compute it efficiently.
What is LCM?
The definition of **LCM** is pivotal for solving related problems. When looking at two integers, the least common multiple refers to the minimal shared multiple resulting from the integers’ multiplication. This is particularly useful when dealing with fractions, adding fractions together requires a common denominator, which can be obtained through the **LCM of fractions**. It ensures streamlined operations in addition or subtraction processes, highlighting the significance of understanding both LCM and GCD (Greatest Common Divisor).
Importance of LCM in Mathematics
Understanding LCM is paramount in mathematics. **LCM rules** aid in simplifying complex operations like adding fractions or scheduling by identifying periods that multiple cycles coincide. It also forms the foundation for further mathematical operations and teaching methods, providing resources to tackle advanced math concepts. Students and professionals alike benefit from mastering LCM as it enhances problem-solving efficiency in various scenarios.
Real-life Applications of LCM
LCM has extensive applications in real-life situations. For instance, if two people are following exercise schedules that repeat every 4 and 6 days respectively, the **LCM of whole numbers 4 and 6** would minimize confusion when determining when they will be able to workout together again. Additionally, in designing puzzles or games, LCM can help create engaging math challenges based on common multiples, enhancing interactive learning.
Methods for Finding LCM: Steps and Techniques
There are multiple techniques to compute the LCM with varying complexities and efficiency. Depending on the scenario or convenience, you can utilize methods such as **LCM using division method, LCM by listing multiples,** or even **LCM by prime factorization.** Each method allows individuals to approach LCM calculations in a structured manner, making it accessible and user-friendly for students and teachers alike.
LCM by Prime Factorization
Using **LCM by prime factorization** is an effective mathematical technique. This method involves breaking down each number to its prime factors. For instance, to find the LCM of 60 and 48, you first express the numbers as products of prime factors. The prime factorization yields: 60 = 2² × 3 × 5 and 48 = 2⁴ × 3. Next, take each prime factor at its highest power: 2⁴, 3¹, and 5¹. Thus, the LCM of 60 and 48 is 2⁴ × 3¹ × 5¹ = 240.
LCM by Listing Multiples
Another straightforward method for computing LCM is **LCM by listing multiples**. This involves listing out the multiples of each number until a common one appears. For example, to find the **LCM of two numbers** such as 3 and 4, you would list the multiples:”
3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, …
4: 4, 8, 12, 16. The first common multiple is 12, so the LCM is 12. This technique is handy for small integers but may be inefficient for larger numbers. Therefore, it’s excellent for educational activities to engage students in understanding multiples.
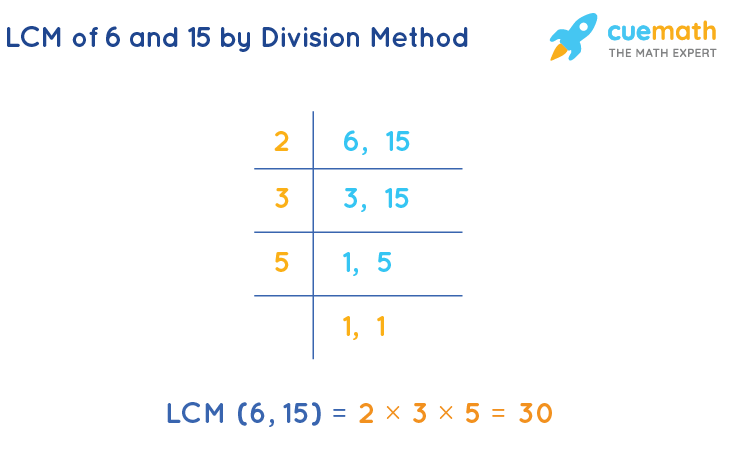
Using Division Method for LCM
The **LCM using division method** involves finding the LCM through systematic division. To illustrate, consider the numbers 18 and 24. Place the numbers side by side and divide them by common prime numbers until only 1’s remain:
2 | 18 24
| 9 12
3 | 9 6
| 3 2
| 1 1.
The LCM is obtained by multiplying all the divisors: 2 × 3 × 3 = 18. This method emphasizes discovering factors efficiently, making it beneficial in various mathematical contexts.
Mind the Details: LCM in Problem Solving
To achieve meaningful results using the **LCM formula**, attention to detail is crucial. Understanding the effective application of LCM in problem solving equips students with a powerful tool that simplifies processes that may initially seem daunting. **Step-by-step LCM** strategies enhance learning and keep engagement levels high.
Step-by-Step LCM: Engaging with LCM Problems
Implementing a clear **step-by-step LCM** approach helps students tackle related problems with confidence. Start by identifying the numbers needed for LCM calculation, apply the correct method, and articulate each step. For instance, if students struggle with **LCM word problems** concerning schedules or collections, guiding their problem-solving process ensures they can articulate their reasoning while learning actively. Practice is key for building fluency with LCM.
Teaching LCM with Visual Aids
Utilizing visual aids strengthens comprehension of **LCM concepts** among learners. This includes diagrams and charts that illustrate concepts in an engaging manner, making learning interactive and effective. Resources designed for fostering understanding not only create a deeper connection with the material but also serve as important educational tools in the classroom environment.
Examples of LCM in Real Life
Before moving into exercises or resources, experiencing **examples of LCM in real life** can solidify comprehension. Whether you’re determining the timing for traffic lights to minimize wait times, syncing schedules between friends, or combining ingredients for a recipe that requires common multiples, the LCM plays a critical role. Life is filled with moments where mastering this mathematical concept can present clear advantages in efficiency and organization.
Resources and Practice Tools for Learning LCM
To help students improve their skills and gain confidence in understanding LCM, various tools and resources are available. Whether through worksheets, quizzes, or even digital calculators, having access to diverse educational materials fosters a comprehensive learning environment. Utilizing these resources reinforces concepts discussed throughout this article and transforms passive knowledge into active application.
Interactive LCM Learning Tools
Technology has made it easier than ever to engage with LCM through **interactive learning tools**. Websites and apps offer exercises tailored to various learning styles. For instance, LCM games and quizzes can be riveting and instructive, providing students with immediate feedback on their calculations and methods while also reinforcing learning objectives through playful interaction.
LCM Worksheets and Practice
Worksheets are essential for structured practice in mastering LCM. Resources categorized as **LCM worksheets** often include a variety of exercises that require students to find the LCM using different methods. This practical application – mixed with challenges – aids retention and comprehension of **finding LCM** in real-world scenarios. Completing these exercises will enhance competence and confidence.
Assessment and Feedback
Incorporating periodic assessments of LCM knowledge through quizzes provides valuable feedback for improvement. Identifying specific areas of struggle highlights topics needing further review—ensuring students are well-prepared for more complex math concepts in a supportive manner. These assessments bolster understanding, shape learning paths, and encourage deeper engagement and mastery of the **LCM properties**.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding LCM is essential for successful mathematical operations, especially in fractions and scheduling.
- Different methods, such as listing multiples and prime factorization, provide flexibility in calculating LCM.
- Real-life applications of LCM, from traffic to recipes, showcase its relevance and importance.
- Interactive tools and worksheets are valuable resources for reinforcing understanding of LCM.
- Practice and assessment tools build confidence and proficiency in handling LCM problems.
FAQ
1. How can I calculate LCM effectively without a calculator?
A practical way to calculate **LCM without a calculator** is to use the prime factorization method. Break down the numbers into their prime factors and identify the highest powers of each prime, multiplying them together. Additionally, listing multiples can also help if the numbers are small.
2. What are some common applications of LCM in real life?
**Examples of LCM in real life** include scheduling tasks, planning events with repeating cycles, or working with fractions that require a common denominator for addition or subtraction. Understanding how to compute LCM simplifies many everyday activities.
3. What is the relationship between LCM and GCD?
**LCM and GCD** are interrelated concepts; the product of the LCM and GCD of two integers equals the product of those integers. This relationship is essential in various applications, presenting a unique advantage in problem-solving scenarios.
4. Can LCM be calculated for more than two numbers?
Yes, **finding LCM for more than two numbers** can be accomplished by determining the LCM of two numbers first, then calculating the LCM of the result with the next number. This process continues until all numbers are accounted for. The methods remain the same, but the calculation is carried through each step.
5. Are there LCM games or exercises for practice?
Numerous **LCM games and exercises** are available online and in educational resources, which engage students while testing their understanding. They promote learning through problem solving in an enjoyable format, allowing practical experience with concepts surrounding the least common multiple.