“`html
Effective Ways to Calculate Degrees of Freedom in 2025: Understand the Essentials
Understanding the Basics: Degrees of Freedom Definition
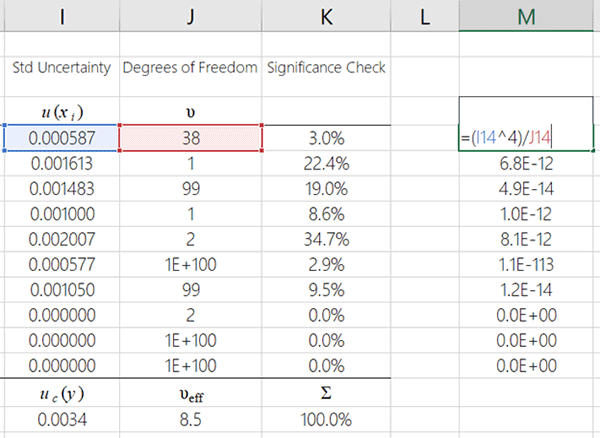
The concept of degrees of freedom is fundamental in statistics and data analysis. It refers to the number of independent values or quantities that can be assigned to a statistical distribution. Essentially, degrees of freedom can help to determine the number of values in a calculation that are free to vary. For instance, in hypothesis testing, understanding degrees of freedom significance is paramount as it influences the shape of distributions used to calculate p-values and confidence intervals. As researchers and practitioners in various fields grapple with this concept, grasping the basic concepts of degrees of freedom is vital for accurate statistical analyses.
Degrees of Freedom in Statistical Testing
When you conduct statistical tests, such as t-tests or chi-squared tests, the application of degrees of freedom is crucial. For example, in a t-test, degrees of freedom are calculated based on the number of samples minus one. This adjustment accounts for the variability within the data and ensures that hypothesis testing is accurate. Understanding how to use degrees of freedom appropriately will enhance the validity of your conclusions.
The Relationship between Sample Size and Degrees of Freedom
There’s a direct relationship between sample size and degrees of freedom. Larger sample sizes typically lead to higher degrees of freedom, thereby enhancing the reliability of statistical analyses. It’s essential to understand how alterations in your sample size affect the degree of freedom in hypothesis testing explained, as this can significantly impact the outcomes of your tests, adding robustness to inferential statistics.
Calculating Degrees of Freedom for Different Data Sets
Calculation methods vary with the type of data set being analyzed. For example, when dealing with simple linear regression, degrees of freedom can be calculated as the total number of observations minus the number of parameters being estimated. Understanding how to determine degrees of freedom is critical across various contexts, especially in calculating degrees of freedom for different data sets can lead to more accurate interpretations of results.
Practical Examples of Degrees of Freedom Calculation
To clarify how to calculate degrees of freedom, consider a practical example involving a dataset with five observations. If estimating the mean, the degrees of freedom would be calculated as 5 (the total number of observations) minus 1 (the estimated parameter), resulting in 4 degrees of freedom. This process is essential in conveying the importance of degrees of freedom in statistics, especially in ensuring the reliability of test statistics.
Factors Influencing Degrees of Freedom
Several elements can influence the computed degrees of freedom, including the number of groups compared and the design of the experiment. In the context of degrees of freedom in experimental design, knowing how to adjust for these factors can help refine the analysis and lead to better decision-making within experiments. If a researcher fails to accurately account for these elements, it can result in systematic errors in degrees of freedom calculation.
Implications of Degrees of Freedom in Model Interpretations
Incorporating degrees of freedom into your models not only allows for better data analysis but also offers insights into the behavior of statistical models. For instance, in multiple regression analysis, the degrees of freedom must be adjusted based on the number of variables considered, which directly impacts the model’s validity. Understanding the implications of degrees of freedom can assist practitioners in designing more meaningful research.
Degrees of Freedom in Linear Models
Degrees of freedom play a critical role in degrees of freedom in linear models as well, allowing for enhanced accuracy in predictions. In linear regression, the total degrees of freedom are divided into regression degrees of freedom and residual degrees of freedom, each playing a crucial role in interpreting the model results. Properly managing degrees of freedom can lead to improved statistical power and insights in predictive modeling.
Common Misunderstandings of Degrees of Freedom
Many newcomers to statistics face challenges regarding the interpretation of degrees of freedom. Common misunderstandings include conflating it with sample size or neglecting its influence on model results. Addressing these misconceptions is vital for statistical literacy, making it imperative to educate learners on misunderstanding degrees of freedom, helping them navigate common pitfalls.
Enhancing Statistical Power with Optimal Degrees of Freedom
Striking a balance when determining optimal degrees of freedom is essential for enhancing statistical power, thereby improving your analyses. Using too many or too few degrees of freedom can lead to misinterpretations of results and statistical inferences. The optimal degrees of freedom situation often arises in large sample contexts, serving to bolster the robustness of your outcomes.
Degrees of Freedom in Quality Control
In the domain of quality control, calculating degrees of freedom can influence decisions made throughout a process. By managing degrees of freedom in quality metrics, businesses can improve their quality control measures while allowing for significant statistical assessments. Applying these concepts, including an understanding of degrees of freedom in quality control, can lead to substantial improvements in manufacturing and operational processes.
Impacts of Degrees of Freedom in Complex Data Analysis
As data complexity increases, so do considerations regarding degrees of freedom. In multivariate analysis, appropriate degrees of freedom calculations become vital for understanding correlations and interactions. Thus, knowledge of degrees of freedom in complex data analysis is essential for data analysts aiming to extract actionable insights from comprehensive datasets.
Key Takeaways
- Degrees of freedom is a crucial concept in statistical analysis that denotes the number of independent pieces of information in a dataset.
- Accurate calculation of degrees of freedom impacts hypothesis testing, ensuring valid statistical conclusions.
- Sample size directly affects degrees of freedom, which in turn influences the accuracy of test results in various statistical contexts.
- Misunderstandings about degrees of freedom can lead to inaccurate interpretations in both simple and complex analyses.
FAQ
1. What is the degrees of freedom definition?
Degrees of freedom refers to the number of values or observations in a statistical analysis that are free to vary. It is sometimes defined as the total number of observations minus the number of parameters estimated. This concept is essential in various statistical tests and models.
2. How to determine degrees of freedom in a t-test?
The degrees of freedom for a t-test can be determined by taking the total number of samples, adding their values together, and subtracting this total by 1. For a two-sample t-test, it is calculated by adding the two sample sizes and subtracting 2.
3. Why are degrees of freedom significant in hypothesis testing?
Degrees of freedom are significant in hypothesis testing because they impact the distribution used when conducting tests. This directly affects p-values, confidence intervals, and ultimately the conclusions drawn from the analysis.
4. What are common errors in degrees of freedom calculations?
Common errors in degrees of freedom calculations include incorrect sample size adjustments and misunderstanding linear model parameters. These errors can lead to misinterpretations of data and flawed conclusions in statistical inference.
5. How does sample size relate to degrees of freedom?
A larger sample size generally results in higher degrees of freedom. This relationship enhances the reliability of statistical analyses and validates findings in hypothesis testing and complex modeling.
“`