Effective Ways to Calculate Percent Yield in 2025
Understanding Percent Yield Definition
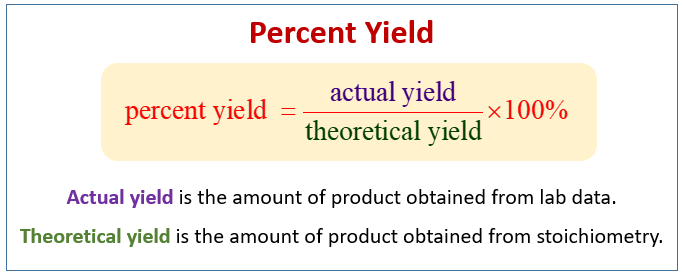
Before diving into how to calculate **percent yield**, it is essential to define what it means in a chemistry context. The percent yield definition refers to the ratio of the actual yield of a product from a chemical reaction to the theoretical yield, expressed as a percentage. The theoretical yield is the amount of product estimated based on balanced chemical equations, assuming 100% conversion of reactants to products. Mastery of the percent yield formula allows chemists and students alike to gauge their process efficiency in various reactions. Understanding this concept serves as a foundation for improving experimental procedures, troubleshooting issues, and engaging effectively in chemical synthesis.
Percent Yield Formula in Detail
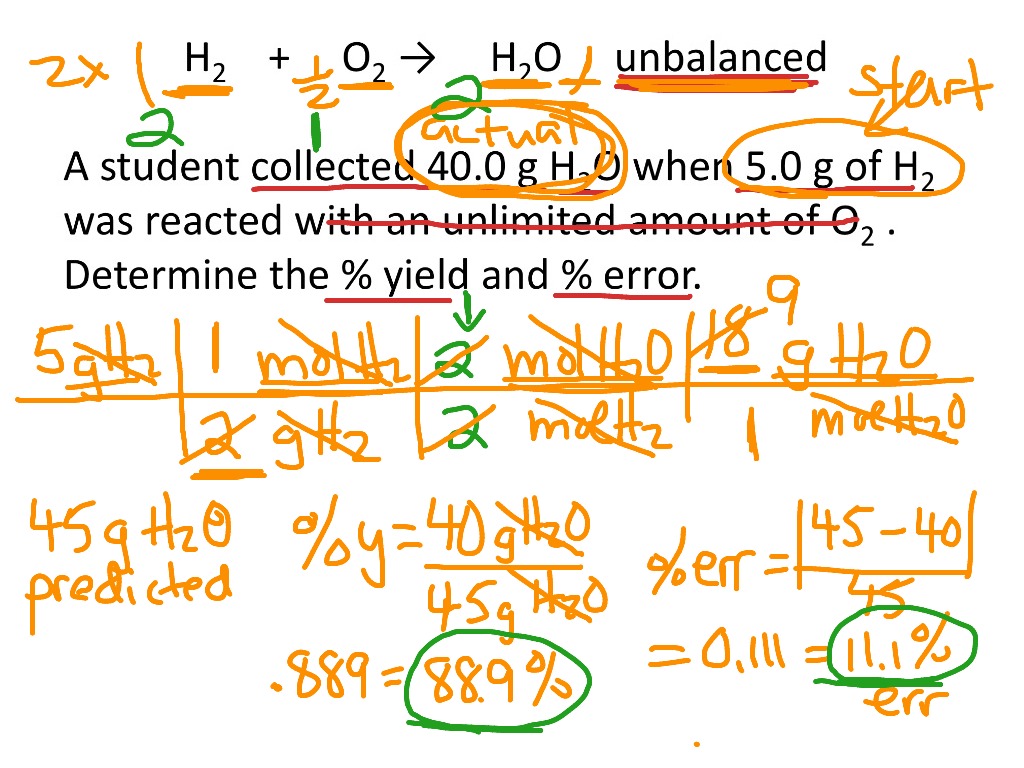
The standard percent yield formula is: Percent Yield = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) x 100%. To put this into practice, consider a reaction where the theoretical yield of product is 50 grams, but only 40 grams are obtained in reality. In this case, the calculation would be: (40g / 50g) x 100% = 80% percent yield. Such applications of the formula help in addressing percent yield problems encountered in laboratory settings. It’s a straightforward calculation that plays a crucial role in percent yield analysis.
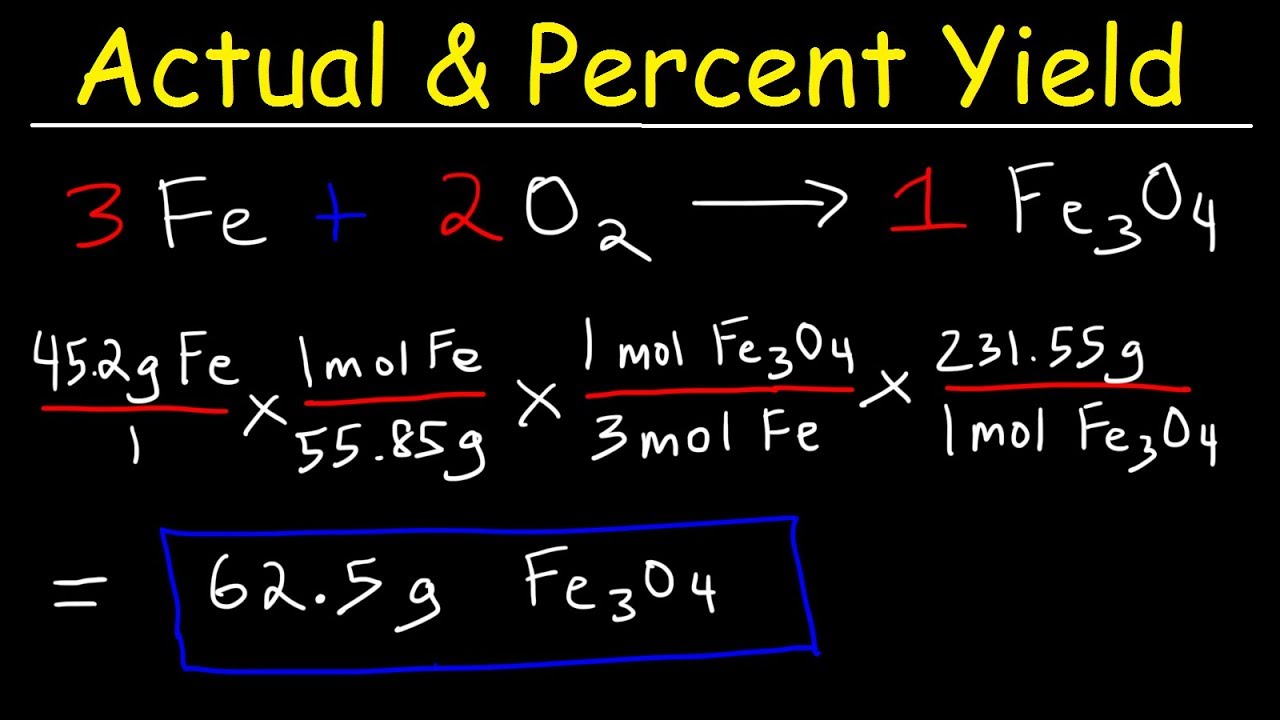
Calculating Percent Yield in Stoichiometry
One common area where calculating percent yield becomes vital is in **stoichiometry**. A proper understanding of stoichiometric coefficients allows for accurate determination of the theoretical yield of a reaction. For instance, in a synthesis reaction, if the coefficients indicate that 2 moles of A produce 1 mole of B, knowledge of initial reactant amounts can help determine theoretical production as well as assess the **percent yield in reactions**. Many chemistry equilibria focus on maximizing efficiency, making the relationship between reactants and products particularly relevant.
Improving Percent Yield Techniques
Improving **percent yield** is crucial for chemistry experiments, especially in industrial settings where cost and resource management is essential. Strategies to enhance yield involve optimizing reaction conditions, selecting appropriate catalysts, and refining purification processes. Increasing temperature, changing solvents, or employing pressure can substantially affect reaction outcomes, and consequently, the final percent yield value. Understanding various factors affecting percent yield can also aid in increasing productivity efficiently.
Common Factors Influencing Percent Yield
Numerous elements can influence the outcome of an experiment, one such factor being **impurities in reactants**. They can cause undesirable side reactions leading to a decrease in actual product recovery. Another significant element affecting success is **reaction time**; insufficient time may not allow reactants to convert fully, resulting in a lower percent yield. Hence, addressing these factors, alongside constant monitoring of conditions, is crucial in achieving consistent improvements in **percent yield**.
Utilizing Percent Yield Worksheets and Exercises
Utilizing tools such as a percent yield worksheet can significantly aid students and practitioners in internalizing concepts. These worksheets typically include various scenarios with related questions requiring percent yield calculations. Working through them enables learners to practice effectively, leaving them familiar with terms like **experimental percent yield**, thus honing their skills in both **basic concepts of percent yield** and practical applications in laboratory settings.
Practical Applications of Percent Yield in Industry
Understanding and mastering **percent yield** calculation is not just restricted to academic chemistry; it has several practical applications in various industries including pharmaceuticals, agribusiness, and manufacturing. These sectors often depend on high yield to ensure economic viability. Implementing reliable methods for **calculating percent yield for reactions** can lead to better resource management, resulting in cost savings and more sustainable processes across numerous applications.
Impact of Percent Yield on Cost Efficiency
In many domains, a higher **percent yield** directly correlates with cost efficiency. For instance, in pharmaceutical manufacturing, achieving a high yield during drug formulation not only reduces production costs but also allows for more effective allocation of resources—enhancing overall productivity and profitability. As such, businesses strive to optimize their formulas continually, evaluate **yield improvements**, and adapt their operational approaches based on calculated yields.
Real-life Examples of Percent Yield Applications
In **real-life examples of percent yield**, consider the synthesis of aspirin, where chemists seek to maximize product output. A laboratory experiment may yield 75% efficiency by adjusting reaction conditions and changing raw material quality. Investigating the different steps in the formulation process and their contribution to the **experimental percent yield** showcases the importance of precise calculations and continuous assessment in ensuring successful results. By integrating findings, laboratories can develop protocols that enhance output and maximize the use of materials efficiently.
Common Errors and Limitations in Percent Yield Determination
Even with extensive knowledge of finding percent yield, various errors can occur during the process, impacting the accuracy of results. A basic understanding of such **percent yield errors** is crucial for mitigation strategies. Consider, for example, human errors in measurement or calculation, which can skew both actual and theoretical yields. Therefore, implementing rigorous quality control can significantly minimize such discrepancies, leading to reliable assessments.
Correcting Common Sources of Error
To optimize yields further, identifying common **sources of error in percent yield** calculation can lead to more accurate experimental results. Errors may arise from incorrect weighing of reagents, miscalculations, or assumptions about expected reaction outputs. Implementing practices such as cross-verification of measurements and peer-review checks during the reporting of yields helps in reducing these occurrence rates—establishing greater trust in the validity of results.
Factors Contributing to Limitations in Percent Yield
Understanding the limitations of the standard **percent yield** equation is beneficial, as it frequently assumes ideal conditions. In real-world practices, factors such as reaction conditions, completion of reaction, and efficient purification techniques may impact the reliability of yields observed. Recognizing and questioning these limitations enable chemists to persist in refining their methodologies and striving for greater experimental fidelity in this vital concept.
Key Takeaways
- Mastering the **percent yield calculation** is crucial in chemistry for evaluating reaction efficiency.
- Identifying and correcting common **percent yield errors** can greatly enhance experimental outcomes.
- Real-life applications demand high percent yields, directly influencing economic efficiency across various industries.
- Resources such as worksheets and exercises serve as effective aids for learning and improving yield calculations.
- Continued practice and refinement are necessary for achieving consistent improvements in yield calculations.
FAQ
1. What is percent yield in chemistry?
Percent yield in chemistry is defined as the ratio of the actual yield to theoretical yield, expressed as a percentage. This calculation helps assess efficiency in reactions, where a value close to 100% indicates a highly efficient reaction.
2. How do you calculate percent yield?
The calculation of **percent yield** is performed using the formula: Percent Yield = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) x 100%. This equation allows chemists to quantify reaction outcomes effectively.
3. What is the significance of percent yield?
The significance of **percent yield** lies in its ability to showcase the efficiency of a chemical process, guiding improvements in experimental design, operational methods, and resource allocation across industries.
4. What common errors impact percent yield calculations?
Some common errors impacting **percent yield calculations** include measurement inaccuracies, loss of product during purification, side reactions, and incorrect estimation of theoretical yield. Awareness of these errors is vital to ensuring accurate reporting.
5. Are there practical applications of percent yield in industries?
Indeed, **practical applications of percent yield** in industries include pharmaceuticals, where higher yields reduce costs and improve resource optimization, ultimately enhancing productivity and sustainability in production processes.
6. How can I improve my percent yield results?
One can improve **percent yield results** by optimizing reaction conditions, using quality reagents, refining purification processes, and consistently performing detailed assessments of factors affecting yield in experiments.
7. What is the difference between theoretical yield and percent yield?
Theoretical yield refers to the maximum amount of product predicted by stoichiometric calculations, while **percent yield** is the actual amount produced expressed as a percentage of the theoretical yield, providing insight into the efficiency of the reaction.