“`html
Effective Ways to Find the Vertex of a Quadratic Function
Understanding the Vertex of a Quadratic Function
Finding the vertex of a quadratic function is crucial for analyzing its properties, especially when dealing with parabolas. The vertex serves as a turning point in the graph of the quadratic. It helps determine whether the parabola opens upward or downward, indicating the presence of a maximum or minimum value quadratic based on the leading coefficient. This section explores the foundational aspects of quadratics, including the significance of the vertex coordinates and the different forms of quadratic functions.
The Vertex Characteristics and Properties
The vertex of a quadratic function, represented in standard form as f(x) = ax² + bx + c, can be crucial for graphing quadratic equations. Its geometric interpretation typically involves assessing the axis of symmetry and how it affects the graph’s shape. The standard approach to identify the vertex is using the vertex formula, which provides a succinct method to derive the vertex coordinates directly: x = -b/(2a). The corresponding y-coordinate can then be calculated by evaluating f(x).
Transformations of Quadratic Functions
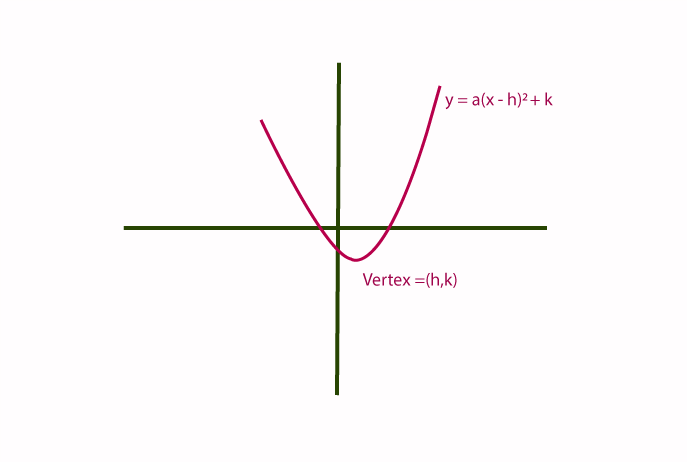
The transformation of quadratics plays a vital role in how we visualize the vertex in quadratic graphs. For instance, when shifting a parabola left or right, this impacts the vertex’s x-coordinate. Furthermore, the vertex form of a quadratic, expressed as f(x) = a(x – h)² + k, directly indicates the vertex at (h,k). Understanding these transformations allows for a more grounded interpretation of quadratic functions and facilitates easier calculations when modifying their properties.
Graphing Quadratic Functions and Their Vertices
Graphing quadratic functions can be simplified by first pinpointing the vertex point calculation. Once the vertex is determined, along with any x-intercepts identified through the quadratic formula, you can visualize the full parabolic curve. Expressing quadratics in vertex form conversion not only helps in sketching graphs but also enhances understanding of their application in graphs and further optimizes performance in real-life scenarios, such as optimizing profit functions in business applications.
Methods to Find the Vertex Algebraically
There are multiple strategies for determining the vertex of a quadratic. Each method has specific scenarios where it may be most effective. Let’s explore these techniques in detail.
Using the Quadratic Formula to Find Vertex
Utilizing the quadratic formula vertex gives an algebraic method of solving for the roots that simultaneously unlocks insights into the vertex’s position. When equations are structured in standard form, substituting into the formula allows one to derive the specific vertex coordinates by determining x first and then y. This method ensures a solid grasp of both the structure of the function and its graphical representation.
Finding Vertex by Completing the Square
A powerful approach to locate the vertex involves finding vertex by completing the square. This method reconfigures any standard quadratic equation into its vertex form. For instance, converting f(x) = ax² + bx + c to f(x) = a(x – h)² + k splits the expression into perfect squares. The vertex becomes apparent as (h,k). This process emphasizes the underlying mechanics of a parabola and reinforces understanding through visual proofs.
Finding Vertex from Intercepts
Another practical technique involves discovering the vertex from intercepts. By calculating the midpoints between the x-intercepts, one can effortlessly determine the x-coordinate of the vertex. Consequently, evaluating the quadratic at this midpoint yields the y-coordinate. This method not only solidifies the relationship between the graph’s intercepts and vertex but also enhances computations involved in solving equations.
Real-World Applications of Quadratic Functions
The application of vertex in graphs extends beyond mere mathematics into fields such as physics, engineering, and economics. Analyzing various scenarios where quadratics are applicable bolsters appreciation for their significance.
Using Vertex in Mathematical Modeling
In many real-life contexts, identifying the vertex in mathematical modeling can offer insight into optimization problems, such as maximizing a specific resource or determining the most efficient route. For example, an architect may use quadratic equations to model the optimal height of parabolic arches, integrating vertex analysis into construction. This promotes a deeper understanding of how variety in quadratics relates directly to functional behavior.
Applications of Quadratics in Physics
Physics applications of quadratics often depend on analysing projectile motion. When calculating the trajectory of an object, the apex or vertex represents the maximum height. Understanding this vertex can be integral in designing sports equipment that optimizes performance, such as basketball arcs or javelin throws, demonstrating the impact of quadratic functions tangibly.
Quadratics in the Economic Field
In economics, the *vertex of quadratic functions* is commonly implemented in techniques identifying break-even points or maximum profit scenarios. By formulating pricing models or inventory optimization strategies, businesses utilize quadratic equations to navigate decision-making landscapes effectively. This intersection serves as a practical foundation linking academic theory with real-world implications.
Key Takeaways
- The vertex is a critical aspect of understanding and graphing quadratic functions.
- Multiple methods exist for determining vertices including the quadratic formula and completing the square.
- Real-world applications of quadratics highlight their functional significance
- Vertex understanding facilitates optimization in various fields such as physics, economics, and architectural design.
- Transformational knowledge enhances quadratics’ application in contextual scenarios.
FAQ
1. What are the vertex coordinates in a quadratic function?
The vertex coordinates refer to the point on the graph where the parabola changes direction. For a standard form quadratic equation f(x) = ax² + bx + c, the vertex can be calculated using the formula x = -b/(2a) to determine the x-coordinate, and substituting it back into the equation gives the y-coordinate.
2. How can I transform a standard quadratic to vertex form?
To convert from standard form to vertex form, you will typically complete the square. Starting with the standard quadratic equation f(x) = ax² + bx + c, you rearrange it to highlight perfect squares, ultimately transforming it into the vertex form: f(x) = a(x – h)² + k, where (h, k) represents the vertex point.
3. Why is the vertex important in graphing quadratic functions?
The vertex holds significant importance as it indicates either the maximum or minimum point of the parabola, aiding in accurately sketching the graph. Knowing the vertex also simplifies the understanding of the entire function’s behavior, including its turning points and overall shape.
4. Can the vertex be found from the x-intercepts?
Yes, the vertex can often be found from the x-intercepts by determining the midpoint between the two intercepts. The x-value at this midpoint represents the x-coordinate of the vertex, and substituting it back into the quadratic function will yield the y-coordinate.
5. What applications do quadratic functions have in real life?
Quadratic functions have diverse applications, including modeling projectile motion in physics, optimizing production or pricing strategies in economics, and assisting in architectural designs where parabolic shapes are crucial. These real-life scenarios demonstrate the functional importance of understanding the vertex.
“`